 English
English Español
Español  Português
Português  русский
русский  Français
Français  日本語
日本語  Deutsch
Deutsch  tiếng Việt
tiếng Việt  Italiano
Italiano  Nederlands
Nederlands  ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย  Polski
Polski  한국어
한국어  Svenska
Svenska  magyar
magyar  Malay
Malay  বাংলা ভাষার
বাংলা ভাষার  Dansk
Dansk  Suomi
Suomi  हिन्दी
हिन्दी  Pilipino
Pilipino  Türkçe
Türkçe  Gaeilge
Gaeilge  العربية
العربية  Indonesia
Indonesia  Norsk
Norsk  تمل
تمل  český
český  ελληνικά
ελληνικά  український
український  Javanese
Javanese  فارسی
فارسی  தமிழ்
தமிழ்  తెలుగు
తెలుగు  नेपाली
नेपाली  Burmese
Burmese  български
български  ລາວ
ລາວ  Latine
Latine  Қазақша
Қазақша  Euskal
Euskal  Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan  Slovenský jazyk
Slovenský jazyk  Македонски
Македонски  Lietuvos
Lietuvos  Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel  Română
Română  Slovenski
Slovenski  मराठी
मराठी  Srpski језик
Srpski језик
What is the basic principle of ball valve?
2024-09-10
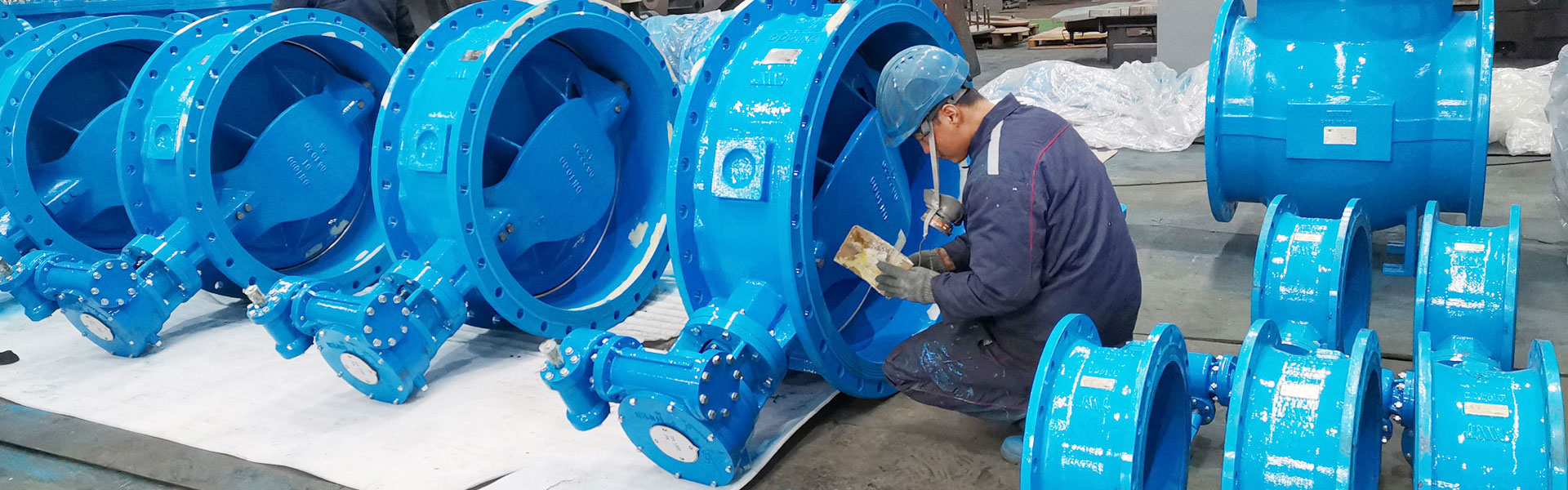
A ball valve operates on the principle of a hollow ball that rotates within a bore. The ball has a hole through it, which allows the flow of liquid or gas through the valve when the hole is aligned with the inlet and outlet ports of the valve. The ball can be rotated 90 degrees in either direction using a handle, which will cause the hole to become perpendicular to the ports and block the flow of fluid.
One of the key advantages of a ball valve is its ability to provide a tight shutoff, as the ball is pressed firmly against the seal when in the closed position. This makes them a popular choice for applications where leakage could have serious consequences, such as chemical processing, oil and gas refining, and power generation.
There are several different types of ball valves, with variations in design depending on factors such as the pressure and temperature of the fluid, the flow rate, and the desired level of control. Some common types include floating ball valves, trunnion-mounted ball valves, and multi-port ball valves.





