 English
English Español
Español  Português
Português  русский
русский  Français
Français  日本語
日本語  Deutsch
Deutsch  tiếng Việt
tiếng Việt  Italiano
Italiano  Nederlands
Nederlands  ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย  Polski
Polski  한국어
한국어  Svenska
Svenska  magyar
magyar  Malay
Malay  বাংলা ভাষার
বাংলা ভাষার  Dansk
Dansk  Suomi
Suomi  हिन्दी
हिन्दी  Pilipino
Pilipino  Türkçe
Türkçe  Gaeilge
Gaeilge  العربية
العربية  Indonesia
Indonesia  Norsk
Norsk  تمل
تمل  český
český  ελληνικά
ελληνικά  український
український  Javanese
Javanese  فارسی
فارسی  தமிழ்
தமிழ்  తెలుగు
తెలుగు  नेपाली
नेपाली  Burmese
Burmese  български
български  ລາວ
ລາວ  Latine
Latine  Қазақша
Қазақша  Euskal
Euskal  Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan  Slovenský jazyk
Slovenský jazyk  Македонски
Македонски  Lietuvos
Lietuvos  Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel  Română
Română  Slovenski
Slovenski  मराठी
मराठी  Srpski језик
Srpski језик
What is the difference between a globe valve and a gate valve?
2025-07-14
As key equipment for controlling the flow of media in a pipeline system, globe valves and gate valves are both cut-off valves, but they differ significantly in structural design, working characteristics and applicable scenarios. Improper selection may affect system efficiency and even cause safety hazards.
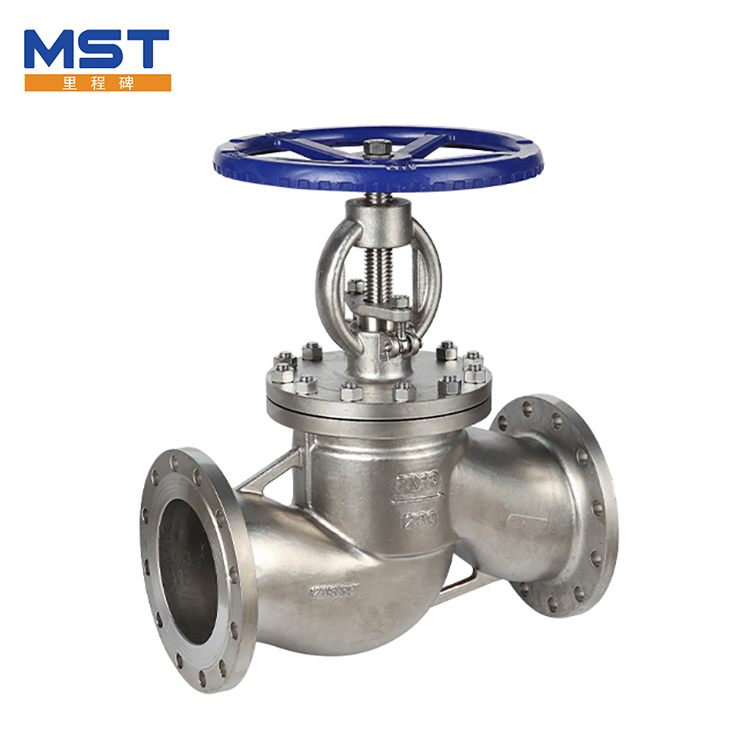

The essential difference in structural design determines the functional characteristics. The globe valve adopts a "valve disc vertical interception" structure. There is a valve seat perpendicular to the direction of the fluid in the valve body. The valve disc moves up and down through the screw rod to achieve sealing. The fluid needs to make a 90-degree turn to flow through the valve body. The flow resistance coefficient (about 3-5) is much higher than that of the gate valve. The gate valve relies on "gate parallel interception". The gate moves vertically along the center line of the valve seat. When fully opened, the gate is completely separated from the flow channel. The flow resistance coefficient is only 0.1-0.5, which is close to the flow capacity of a short pipe.
Flow control and sealing performance each have their own emphasis. The valve disc and valve seat of the globe valve are face-contact seals, and the sealing is more reliable when closed. It is especially suitable for low-pressure small-diameter pipelines (DN15-DN100), and the flow can be accurately adjusted by the valve disc opening. It is often used in occasions that require throttling (such as heating systems). However, its sealing surface is easily damaged by high-speed fluid erosion, and its service life is generally 10,000-20,000 times of opening and closing. The gate of the gate valve is in line contact with the valve seat. There is no throttling loss when fully open. It is suitable for large-diameter pipelines (DN100-DN1000), but it needs to be accurately aligned when closed, otherwise it is easy to leak, and flow regulation cannot be achieved. It is mostly used in fully open and fully closed conditions (such as tap water mains).
The difference in applicable working conditions is obvious. The globe valve is suitable for conveying clean media such as clean water and oil. The working pressure is usually not more than 16MPa, and the temperature range is -29℃ to 425℃. Pay attention to the flow direction (low inlet and high outlet) during installation, otherwise the sealing performance will be reduced. The gate valve can be used to transport media containing a small amount of particles (such as sewage), with a pressure level of up to 42MPa, a wider temperature adaptability range (-196℃ to 540℃), and no directional restrictions on installation, but it is not suitable for frequent opening and closing scenarios, and frequent operation can easily cause the gate to get stuck.
Maintenance cost and service life need to be considered comprehensively. The valve disc and screw rod connection structure of the globe valve are simple, and only the sealing gasket needs to be replaced during maintenance. The single maintenance cost is about 50% of the gate valve. The gate valve has a complex guiding structure between the gate and the valve stem. If it gets stuck, it needs to be disassembled as a whole, and the maintenance time is 2-3 times that of the globe valve. However, in the fully open state, the flow resistance of the gate valve is small, which can reduce the energy consumption of the pipeline and is more economical for long-term use.
When selecting, the basic principle of "selecting a globe valve for a small diameter and a gate valve for a large diameter; selecting a globe valve for flow adjustment, selecting a gate valve for full opening and closing; selecting a globe valve for clean media and a gate valve for media containing particles" should be followed. Only by combining system pressure, medium characteristics and operating frequency can the valve's optimal performance be brought into play and the safe and efficient operation of the piping system be ensured.




